Intravascular ECG P-Wave
Tip Positioning
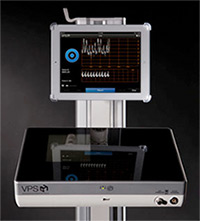
By combining intravascular ECG and intravascular Doppler, the ARROW® VPS G4™ Device represents a paradigm shift away from an external tip confirmation system to an intravascular navigation and tip confirmation system.
Since the 1980s, right atrial ECG has been used to guide the placement of CVCs.9 Studies have shown that the atrial P-Wave grows with increasing proximity to the RA.
Why isn't P-Wave tip positioning always reliable?
P-Wave elevation is correlated to the position of the SA node within the RA. Accuracy of placement can be affected by several factors. For example, anatomical variations in the RA are associated with variations in SA node function, size, shape and location. The angle at which the catheter enters the RA and ECG lead position can both alter the elevation of the P-Wave.
Human interpretation of ECG waveform can vary and P-Waves themselves can be abnormal, as in the case of atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or atrial ectopic heartbeat.
Atrial P-Wave grows with increasing proximity to the RA

Thus, ECG alone can be unreliable for determining catheter tip placement in the SVC. The solution is to add a second physiological monitoring system along with ECG.