Factors Affecting Catheter
Tip Placement
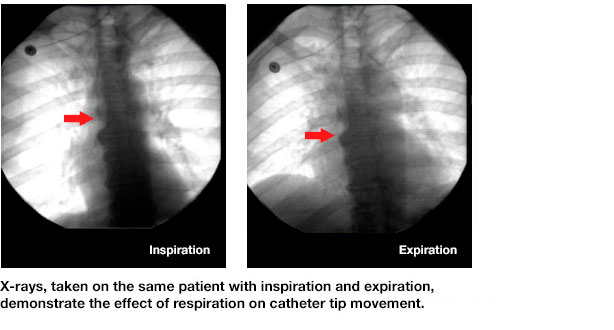
Simple body movements or respiration can cause catheter tips to move up or down, increasing the risk for adverse events. For example, abduction and adduction of the arms can move a catheter tip 2-4 cm up or down.6 Respiration and a supine body position can also cause a catheter tip to move several centimeters from its ideal location.
Catheter tip movement during respiration
Tips placed within the mid-SVC have been linked to increased risk of migration, venous thrombosis, occlusion and loss of access, catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI) and SVC erosion and perforation. Tips located in the upper right atrium (RA) have been linked to catheter-induced arrhythmia, tricuspid valve dysfunction, atrial thrombus formation or embolism, and erosion or perforation of the RA wall.5,7,8
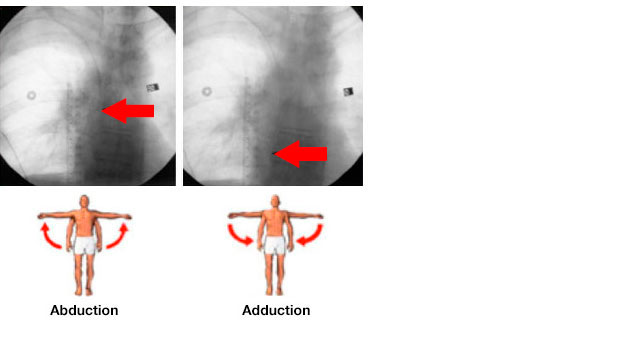
It is well established that arm position affects catheter tip position. Again, note X-rays on the same patient illustrating variable arm positions. Abduction causes tip position to move higher in the SVC, while adduction positions the tip lower inside the patient.
Catheter tip displacement after arm movement
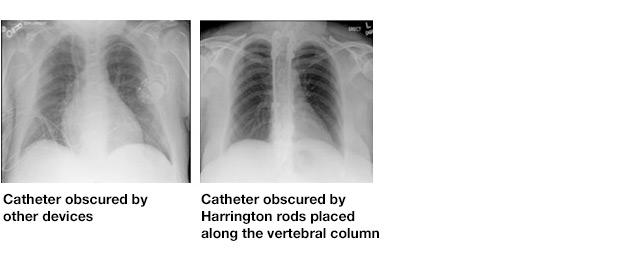
Although X-ray remains the gold standard for catheter tip placement, another variable in accurate readings are the number of other devices the patient has received. It is difficult to accurately detect the tip position when catheters, ECG wires, pacemakers, Harrington rods, etc., are also in the view of the X-ray.
Catheter tips can be obscured by other devices
Parallax

A further limitation of chest X-ray is parallax. Parallax is the apparent shift in the position of an object by a change in the observation position. The brain subconsciously uses information from both eyes to estimate distances. The distance estimate requires observation from two points.
Skeletal structures are not located in the same anatomic plane as the SVC. Therefore, as a result of parallax, the use of these structures as radiographic landmarks can lead to substantial errors in tip positioning.